Have you ever looked at the roof of a house and imagined, “What makes it so special?” You might have noticed the elegant, triangular shape of a gable roof and thought, “That’s a classic design!” Well, you’re right. Gable roofs are classic and useful, but there’s so much more to them than just a pretty face.
If you live in Brooklyn, NYC, or are planning to build or renovate a home here, understanding gable roofs can make all the difference. Gable roofs have many advantages, whether you’re thinking about how they look, how much they cost, or how long they last in this specific climate. So, why should we explore what makes this roof style such a popular choice? Let’s discuss it!

Quick View of Key Informations
- Gable Roof Design: Two sloping sides meeting at a ridge, forming a triangular shape.
- Materials Used: Wood, engineered wood, steel, plywood/OSB, and roofing materials like shingles, metal, or tiles.
- Cost: Installation costs in Brooklyn range from $6 to $9 per square foot.
- Durability: Gable roofs last 20 to 50 years with proper maintenance.
- Design Types: Includes front, side, cross, Dutch, jerkinhead, and saltbox gable designs.
- Attic Space: Gable roofs provide extra attic space for storage or living areas.
- Energy Efficiency: Allows for good ventilation, reducing cooling costs.
- Maintenance: Regular checks for damage, cleaning gutters, and replacing missing shingles.
- Weather Resistance: Handles rain and snow well, but may need reinforcement in high winds.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Adds a balanced, classic look that suits various architectural styles.
What is a Gable Roof?
A gable roof is a classic roof design characterized by two sloping sides that meet at the top to form a ridge, which creates a triangular shape at each end of the building. It is one of the most popular and simple roof designs in residential architecture. This design not only provides a clean, stylish look but also allows for good water drainage, which makes it practical in areas with heavy rainfall or snow. The shape of the gable roof can vary depending on the pitch.
Materials Used for Gable Roof Construction
Building a strong and durable gable roof requires the right materials, each playing an important role in ensuring the roof lasts for years. Let’s look at the materials commonly used for gable roof construction:
- Wood (Lumber or Timber): The primary material used for framing the roof, such as the rafters, ridge board, and collar ties. Wood is lightweight, strong, and affordable, which makes it a common choice for residential homes. It can be easily cut to size and shaped for a custom roof design.
- Engineered Wood (LVL or Glulam): These materials offer superior strength, especially for larger spans. They are more durable than traditional wood and less prone to warping or shrinking over time. Engineered wood is often used for the ridge beam or rafters in larger buildings.
- Steel or Metal: Used in larger gable roofs or commercial buildings, steel and metal provide a durable, long-lasting option that resists harsh weather conditions. Lightweight and fire-resistant metal frame is ideal for explosive environments.
- Plywood or OSB (Oriented Strand Board): These materials are used for the roof decking or sheathing. It provides a solid base for the roofing material. They are relatively inexpensive and easy to install while providing excellent strength and stability.
- Roofing Materials (Shingles, Metal, or Tiles): The outer layer of the roof can be made from various materials like asphalt shingles, metal panels, or clay tiles. Shingles are the most common for gable roofs because of their affordability and ease of installation, while metal and tiles provide durability and a unique aesthetic.
What Are the Different Designs of Gable Roofs?
When it comes to gable roofs, there’s no one-size-fits-all. The design of the gable roof can vary based on the desired look, functionality, and the type of building. Let’s explore some popular gable roof designs and their unique features:
Front Gable
- Description: In this design, the ridge runs parallel to the street, and the gable faces the front of the house. It’s often used in traditional and colonial-style homes.
- Features:
- Symmetrical design with a prominent gable at the front.
- Gable walls are often decorated with windows or trim.
- The ridge is positioned along the length of the building.
- Easy to recognize due to the clear triangular shape at the front.
- Advantages:
- Provides an attractive and balanced façade.
- Enhances curb appeal.
- Ideal for homes that want a classic look.
- Allows for natural light through front-facing windows.
- Ideal For: Traditional, Colonial-style homes, and residential buildings looking for a classic appearance.
Side Gable
- Description: The ridge runs perpendicular to the street, and the gable is positioned on one of the sides of the building. This is the most common gable roof design.
- Features:
- Simpler and more streamlined look.
- Two sloping roof planes meet at the ridge, forming a triangular end on each side.
- More flexible in terms of interior space.
- Common in modern and minimalist homes.
- Advantages:
- Simple to design and construct.
- Cost-effective for standard residential buildings.
- Offers a good amount of attic space.
- Works well with a variety of architectural styles.
- Ideal For: Traditional homes, modern homes, and structures with narrow lots.
Cross Gable
- Description: Two gable roofs intersect at right angles, which form a T-shaped or L-shaped structure. This design creates a more complex and dynamic roofline.
- Features:
- Two separate roof sections joined at a right angle.
- Multiple gable ends create a more intricate and interesting appearance.
- Allows for more interior design flexibility.
- Ideal for larger buildings or homes with multiple sections.
- Advantages:
- Adds architectural interest and depth to the design.
- Provides extra space in larger homes.
- Works well for homes with wings or extensions.
- Increased design flexibility for complex structures.
- Ideal For: Larger homes, T-shaped or L-shaped floor plans, and multi-sectioned buildings.
Dutch Gable (Gablet)
- Description: This hybrid roof combines a gable and a hip roof, where the main roof is hipped, but a small gable is placed at the top.
- Features:
- A small, decorative gable is added to a hipped roof structure.
- Provides the aesthetics of a gable with the stability of a hip roof.
- The gable is typically placed at the peak of the hipped roof.
- Often used in homes that require both visual appeal and structural stability.
- Advantages:
- Offers enhanced wind resistance compared to a standard gable.
- Aesthetically pleasing and adds a unique design element.
- Provides additional height and space in the attic.
- Works well for homes in areas with high wind conditions.
- Ideal For: Homes in windy areas, modern or European-style homes, and those looking for a unique roof design.
Jerkinhead (Clipped Gable)
- Description: A clipped or truncated gable, where the peak of the gable is cut off, creating a less sharp triangular appearance.
- Features:
- The gable’s peak is clipped off to form a more rounded top.
- The design combines gable aesthetics with the stability of a hip roof.
- Reduced wind resistance makes it ideal for storm-prone areas.
- Offers a slightly more subtle, less dramatic profile.
- Advantages:
- More wind-resistant than a typical gable roof.
- Provides a softer, more subtle design.
- Still retains the benefits of gable roofing, such as attic space and ventilation.
- Works well for homes in coastal or high-wind areas.
- Ideal For: Homes in areas with high winds, coastal regions, or homes looking for a unique design element.
Saltbox Gable
- Description: A variation of the gable roof where the back side is much longer and steeper than the front. It creates an asymmetrical look.
- Features:
- The back slope is much longer and steeper than the front slope.
- The front slope is shallower and shorter than the rear.
- Often seen in historic colonial and early American architecture.
- Perfect for creating a distinctive, old-fashioned style.
- Advantages:
- Ideal for regions with heavy snowfall due to the steep back slope.
- Adds a historical charm to the building.
- Provides additional space in the attic or upper floor.
- Great for homes looking for a classic New England aesthetic.
- Ideal For: Colonial-style homes, homes in snowy regions, and those wanting a historical look.

Why Choose a Gabled Roof for Your Greenhouse Design?
Gable roofs are a fantastic option for greenhouses due to their practical design. They allow plenty of sunlight to enter through the sloping sides. It creates the perfect environment for plants. Water drainage through the sloped design reduces water damage and pooling. Plus, the extra attic space can be used for ventilation, which is crucial in maintaining the ideal temperature for your plants.
What Are the Different Shapes of Gable Roof?
Gable roofs come in several shapes, each offers a unique look and functional benefit. The shape of a gable roof can be adapted to suit different architectural styles, climate needs, and personal preferences. Here are the most common shapes of gable roofs you’ll encounter:
- Symmetrical Gable Roof: This is the classic gable roof, with two equal sloping sides meeting at a central ridge. The symmetrical design gives a clean, balanced look to the structure. It is one of the most traditional and widely used roof shapes in residential homes.
- Asymmetrical Gable Roof: A steeper or longer side of the roof creates an angled appearance in this style. This shape is often used to add visual interest and can provide better space utilization in the attic or upper floors. Asymmetrical gable roofs are also great for regions with heavy snow, as the steeper side sheds snow more effectively.
- Dutch Gable (Gablet): A hybrid of a gable and a hip roof, the Dutch gable roof features a small gable at the top of a hipped roof. It combines the beauty of a gable with the stability of a hip roof. This design is great for areas with strong winds, as the hipped portion adds extra stability, while the gable provides a unique look.
- Saltbox Gable: A saltbox gable roof has an asymmetrical design, where the back roof slope is much longer and steeper than the front. This roof style is often seen in Colonial or early American homes. It provides extra upper space and works well in areas with heavy snowfall, as the steep slope helps with snow runoff.
- Gambrel Gable: The gambrel gable is similar to the barn-style roof, with two different slopes on each side of the roof. The lower portion is steeper, while the upper portion has a more gradual slope. This shape maximizes roof space and is ideal for structures that need additional upper-level room.
- Monitor Gable: A monitor gable roof includes a raised section in the middle with a gable design, often used in barns or industrial-style buildings. This raised portion typically features windows to allow for natural light and ventilation. It provides extra interior height and is perfect for structures that require a large amount of space and airflow.
What is Gable Roof Framing?
Gable roof framing refers to the construction of the internal support system that holds up the gable roof structure. It involves carefully placing key components like the ridge board, rafters, and collar ties to form a stable and durable roof. Proper gable roof framing ensures the roof is strong enough to resist various weather conditions and load requirements.
Key Components of Gable Roof Framing
Here are the key components that make up the gable roof framing:
- Ridge Board: The ridge board sits at the peak of the roof, where the two sloping sides meet. It provides a horizontal support point for the rafters and helps keep them aligned. A properly installed ridge board is essential for the stability of the entire roof.
- Rafters: The sloping columns that go from the ridge to the rooftops of a building are called rafters. They form the main support structure for the roof and bear the weight of the roof decking and covering materials. The rafters are spaced evenly and attached securely to the ridge board.
- Collar Ties: These horizontal beams connect opposing rafters near the ridge and prevent the rafters from spreading apart under load. Collar ties also add extra strength to the roof, particularly in areas with heavy snow or wind. They are typically installed about one-third of the way down from the ridge.
- Ceiling Joists: Ceiling joists are horizontal beams that run across the building’s width, parallel to the ridge. They help tie the walls together and provide support for the ceiling below. Ceiling joists prevent the walls from spreading outward due to the pressure from the rafters.
- Gable End Walls: The gable end walls are the vertical walls at each end of the roof, which form the triangular gable ends. These walls support the rafters at the ends of the building and enclose the upper portions of the building. Gable end walls can be designed with windows, vents, or decorative trim.
- Purlins (Optional): Purlins are horizontal beams that run perpendicular to the rafters and help distribute the load evenly. While not always required, purlins are used in larger structures to add extra support to the rafters. They are particularly useful for longer spans where additional support is needed.
What are Gable Roof Trusses?
Gable roof trusses are pre-fabricated triangular frameworks used to support the gable roof structure. They are designed to bear the weight of the roof and distribute it across the walls of the building. Trusses are commonly used for their strength, efficiency, and ease of installation, especially in large homes or commercial buildings. They are manufactured off-site and then delivered to the construction site. It makes the installation process faster and more cost-effective. Gable roof trusses are ideal for larger roof spans and reduce the need for complex on-site framing.
How to Install a Gable Roof
A gable roof installation can seem like a big project, but with the right approach, it’s a straightforward and effective way to complete a roof. The process involves framing the roof structure, adding sheathing, and covering it with roofing materials. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how to install a gable roof:
1. Prepare the Foundation and Walls: Before installing the roof, ensure that the walls are properly built and level. The walls should be square and sturdy enough to support the weight of the roof. Measure and mark the placement for the ridge board and rafters to guide the installation process.
2. Install the Ridge Board: The ridge board is installed at the highest point of the roof. It provides support for the rafters and ensures that the roof stays level. Secure the ridge board to the walls, making sure it’s aligned and properly fixed.
3. Attach the Rafters: Next, install the rafters, which will form the sloping sides of the roof. The rafters should be spaced evenly, depending on the size and design of the roof. Make sure the rafters are securely attached to the ridge board and the top plates of the walls.
4. Install Collar Ties and Ceiling Joists: Collar ties are placed near the ridge to prevent the rafters from spreading apart under load. Ceiling joists are installed to connect the walls and provide support for the ceiling. These components help distribute the weight of the roof more evenly across the structure.
5. Add Roof Sheathing: Once the framework is in place, apply roof sheathing (plywood or OSB) over the rafters. This provides a solid surface for attaching the roofing materials. Make sure the sheets are nailed or screwed securely to the rafters to avoid shifting.
6. Apply Underlayment: Spread a layer of roofing underlayment (felt or synthetic material) over the sheathing to provide an extra layer of protection. This helps prevent leaks and provides a waterproof barrier. Ensure the underlayment overlaps at the edges for a proper seal.
7. Install Roofing Material: Finally, cover the roof with your choice of roofing material, whether shingles, metal, or tiles. Start from the bottom edge of the roof and work your way up. Make sure each row of shingles or roofing panels overlaps the one below it to prevent water penetration.

How Much Does a Gable Roof Installation (per sq ft) Cost in Brooklyn, NYC?
A gable roof in Brooklyn, NYC, involves various factors that influence the overall cost. These include the choice of materials, roof size, complexity of the design, and labor rates. Understanding these costs can help you plan your roofing project effectively.
| Design Type | Material Cost (USD/sq ft) | Labor Cost (USD/sq ft) | Total Cost (USD/sq ft) |
| Basic Gable Roof | $5 – $7 | $3 – $5 | $8 – $12 |
| Cross Gable Roof | $6 – $8 | $4 – $6 | $10 – $14 |
| Dutch Gable Roof | $7 – $9 | $5 – $7 | $12 – $16 |
| Saltbox Gable Roof | $6 – $8 | $4 – $6 | $10 – $14 |
Advantages of Gable Roof
Gable roofs are one of the most popular roof types for residential buildings, and for good reason. They have a lot of advantages that make them seem good and perform well with many different types of buildings. Here are some of the key advantages of gable roofs:
- Simple Design: Gable roofs have a straightforward and clean design. They are easy to construct, which can save on both time and labor costs. This simplicity also provides a timeless look that works well with many architectural styles.
- Excellent Drainage: The sloping nature of gable roofs allows rain, snow, and debris to easily slide off. This makes gable roofs a great option for wet or snowy climates. They reduce the risk of water buildup and minimize the chances of leaks.
- Increased Attic Space
The sloped design of a gable roof provides additional space in the attic, which can be used for storage or even converted into living space. This added space can increase the overall functionality of your home. - Energy Efficiency: The design allows for good ventilation, which helps to reduce heat buildup in the attic during summer. Proper airflow can help lower cooling costs. Additionally, insulation can be easily added to the upper space to improve energy efficiency.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Gable roofs have a symmetrical, balanced design that enhances the appearance of a home. The clean lines and the classic look make gable roofs a favorite choice for homeowners. They are particularly attractive in traditional, farmhouse, and colonial-style homes.
- Cost-Effective: Because of their simple design and ease of construction, gable roofs are often more affordable than more complex roof types. This makes them an excellent option for homeowners looking for an effective and budget-friendly roof design.
- Durability: Gable roofs are strong and can withstand extreme weather conditions, especially when properly installed. The slope helps them handle heavy snowfall and rain, and they can be designed to resist wind and other harsh elements.
Disadvantages of Gable Roof
While gable roofs are a great option for many homes, they also come with a few disadvantages that are important to consider. These drawbacks may influence your decision depending on your home’s location, climate, and aesthetic preferences. Let’s take a look at some of the potential downsides:
- Vulnerability to High Winds: In areas prone to strong winds, gable roofs can be more susceptible to damage. The exposed gable ends are particularly vulnerable, and the roof may be at risk of lifting if not properly secured. Additional bracing may be required for increased wind resistance.
- Snow and Ice Buildup: In snowy regions, the steep slope of a gable roof can lead to the rapid accumulation of snow. While this is great for drainage, it can also cause snow to slide off quickly, potentially damaging gutters, windows, or the foundation. Ice dams may also form at the roof edge, leading to water damage.
- Limited Design Flexibility: While gable roofs are versatile, they can sometimes feel limiting when compared to more complex roof designs. If you’re looking for intricate architectural features, you might need to consider other roof types, such as a mansard or gambrel roof.
- Maintenance Challenges: Gable roofs, especially those with steep pitches, can be challenging to maintain. You might need steps or a framework to clean the gutters and check the roof, which can be risky and expensive. In some climates, the roof may need more frequent care to stay in good condition.
- Exposure to Elements: The triangular gable ends are more exposed to the elements, making them more prone to wear and tear over time. If the gable ends are not well-maintained, they may suffer from rot or damage due to rain and wind, especially if the roof is older.
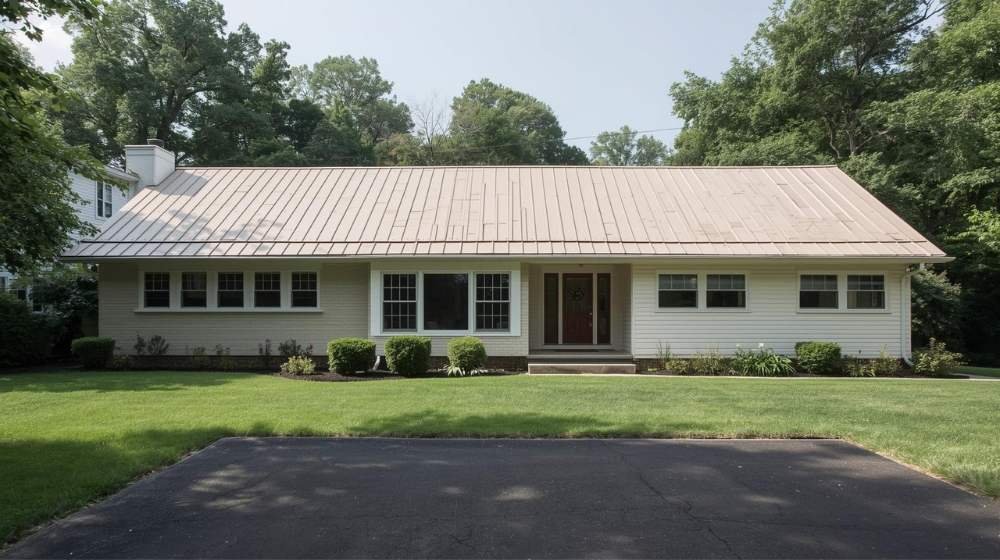

Is Gable Roofing the Right Choice for Brooklyn, NYC?
When considering roofing options for homes in Brooklyn, NYC, a gable roof might just be the ideal choice. The unique design of a gable roof offers excellent drainage, which is particularly beneficial for the rainy and snowy climate of Brooklyn. Its simple construction, cost-effectiveness, and aesthetic appeal make it a popular option for many homeowners.
However, if you live in an area prone to high winds, you may need to reinforce the structure to prevent damage. Overall, gable roofing provides a balance of functionality, beauty, and practicality that fits well with both traditional and modern Brooklyn homes.
Gable Roof vs. Other Roofing Types
When choosing the best roof for your home, it’s important to compare different roof types based on key factors such as cost, durability, maintenance, and outlook. Here’s a comparison of gable roofs versus 5 other common roofing types to help you make an informed decision:
| Roof Type | Initial Cost | Durability | Maintenance | Energy Efficiency | Aesthetic Appeal | Weather Resistance |
| Gable Roof | $6 – $9 per sq ft | High | Low | Good | Classic & Symmetrical | Good (but may need reinforcement in high winds) |
| Hip Roof | $7 – $10 per sq ft | Very High | Moderate | Good | Elegant & Balanced | Excellent |
| Flat Roof | $4 – $7 per sq ft | Moderate | High | Moderate | Modern & Sleek | Poor (may require more maintenance) |
| Mansard Roof | $10 – $15 per sq ft | Very High | Moderate | Good | Classic & Victorian | Excellent |
| Gambrel Roof | $5 – $8 per sq ft | High | Low | Good | Barn-style & Rustic | Good |
| Tiled Roof | $6 – $10 per sq ft | Very High | Low | Excellent | Mediterranean & Stylish | Excellent |
Experts Tips for The Care and Maintenance of Gable Roof
Proper care of your gable roof is crucial for extending its lifespan and keeping it functional through the years. Here are some expert tips to help you maintain your gable roof effectively:
- Inspect the Roof Regularly: Schedule an annual roof inspection to catch any potential issues early, such as damaged shingles or cracks in the ridge.
- Clean Gutters and Downspouts: Clogged gutters can lead to water buildup, which can damage the roof and cause leaks. Keep gutters clear of trash, especially during fall and spring.
- Check for Damaged Shingles: Look for cracked, curled, or missing shingles. Replace any damaged shingles immediately to prevent water from seeping under the roof.
- Trim Overhanging Trees: Trees that touch or hang over the roof can cause damage. Trim branches regularly to prevent them from scraping or breaking shingles.
- Seal Vents and Flashing: Check the flashing around chimneys, vents, and skylights. Over time, the sealant may deteriorate, leading to leaks. Reapply sealant if necessary.
- Ensure Proper Ventilation: Proper ventilation reduces heat buildup and moisture, which can lead to mold or rotting. Make sure your attic is well-ventilated to maintain roof health.

Why should you choose a professional roofing contractor?
Are you looking for an expert roofing contractor in Brooklyn, NYC? SR General Construction has you covered! Our business is located at 8807 Avenue B, Brooklyn, NY 11236, United States, in the Canarsie area.
We proudly serve all areas of Brooklyn with high-quality, durable roofing solutions. From new installations to repairs and maintenance, we provide the best service at affordable prices. Contact us and experience why we’re Brooklyn’s roofing experts!
FAQ
1. What is a gable roof?
A gable roof features two sloping sides that meet at a ridge, which forms a triangular shape at each end of the building. This design is popular for its simplicity and effective water drainage.
2. How much does a gable roof installation cost per square foot in Brooklyn?
The cost typically ranges from $6 to $9 per square foot. It depends on materials and complexity.
3. What materials are commonly used for gable roofs?
Common materials include asphalt shingles, metal panels, and clay tiles. These materials offer durability and aesthetic appeal.
4. How long does a gable roof last?
With proper maintenance, a gable roof can last between 20 to 50 years. It depends on the materials used.
5. How do gable roofs compare to hip roofs?
Gable roofs are simpler and more cost-effective, while hip roofs offer better wind resistance due to their design.
6. Can I install solar panels on a gable roof?
Yes, gable roofs are suitable for solar panel installations, especially when they have a south-facing slope.
7. What is the difference between a gable roof and a gambrel roof?
A gable roof has two symmetrical slopes, while a gambrel roof has two slopes on each side, with the lower slope steeper than the upper.